|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TheWorld and Universal Academy Foundation has for ideal goals to promote the arts, the culture and the peace world-wide.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
...
WUACADEMIA: Vocational Education and Training or VET |
Professional Certificate in |
BIOLOGY |
 |
Charles Darwin in 1868 |
| If your Dream is to become a Biologist, this course in for you. |
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is composed of many subdisciplines unified by five so-called axioms: 1.Cells are the basic unit of life A biologist is a scientist who studies living organisms and their relationship to their environment. Biologists involved in basic research attempt to discover underlying mechanisms that govern how organisms work. Biologists involved in applied research attempt to develop or improve medical, industrial or agricultural processes. |
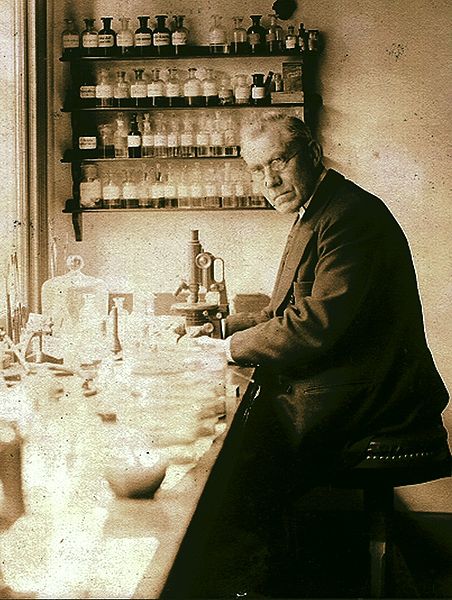 |
Martinus Willem Beijerinck, a Botanist and microbiologist in his laboratory (1921) |
| Do You Want to master Biology? You can! This programm can open doors to careers that you might not have considered. |
REALIZE YOUR AMBITION WITH WUACADEMIA Price €500 (for one year home study) |
| Study Method |
The course is designed for study by distance learning at home or at work. Students will receive all course materials by post or online, plus tutor support by email. |
| Online Learning: |
|
| Qualification |
At the end of this course successful learners will receive a Professional Certificate of achievement. The training courses have been designed specifically to meet the needs of learners who prefer to study from home. |
 |
Plante vivante. Trees (Tsuga heterophylla) and roots in Hoh Rain Forest. |
 |
Les trois âges de la Vie et la Mort, Artwork by Hans Baldung |
 |
Copyright © 2006/2011, Wuacademia/Wuacademy, All Rights Reserved



